Process
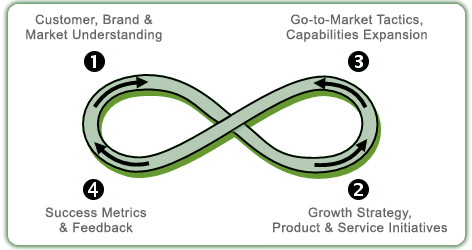
Accelerated Growth System (AGS)Overall, this defined process encourages a disciplined go-to-market approach. Used annually in planning and quarterly in review of tactics, this method has been broadly embraced by senior leaders as well as project managers. This permits all layers of a company to have the same view of expectations and priorities. ENVISION is especially intrigued with empirical (fact-based) growth insights.
Phase 1
Phase 1 is a deep understanding of the existing Customer, Brand, and Market data are collected, analyzed, and conclusions are drawn. A planning Framework is created to serve as the basis to target different segments and create the requirements for products and services. Typically, this is employed to develop a Portfolio Strategy or the ability to create unique offerings to the various market segments. This also permits a deeper competitive and trend assessment.
Phase 2
Phase 2 guides the long term strategic decisions and resource allocations by choosing who you want to serve, which benefits will be offered (against which needs), what intangible assets should be developed, how competitive advantage will be protected and extended, and what competencies (and supporting skill sets) are necessary for success. Plus, the metrics of success must be determined in this phase (e.g., what level of trial, target satisfaction, etc.) so they can be measured in Phase 4.
Phase 3
Phase 3 is all about getting it done—the execution. Tactics are actually organized by ‘Strategic Imperatives’ or the initiatives required to advance the strategies. Therefore, tactics are not addressed individually; rather a proprietary process links the tactics to specific activities, the resources necessary, the time frame for completion, and the person responsible. This allows for a simple and clear management tool to evaluate progress and identify roadblocks.
Phase 4
Phase 4 deals with feedback and progress versus your benchmarks or goals. This is done at two levels: Tangible metrics (e.g., sales, trial, awareness, etc.) and Intangible measures (e.g., satisfaction, value for the money, willingness to endorse or recommend other offerings, etc.).